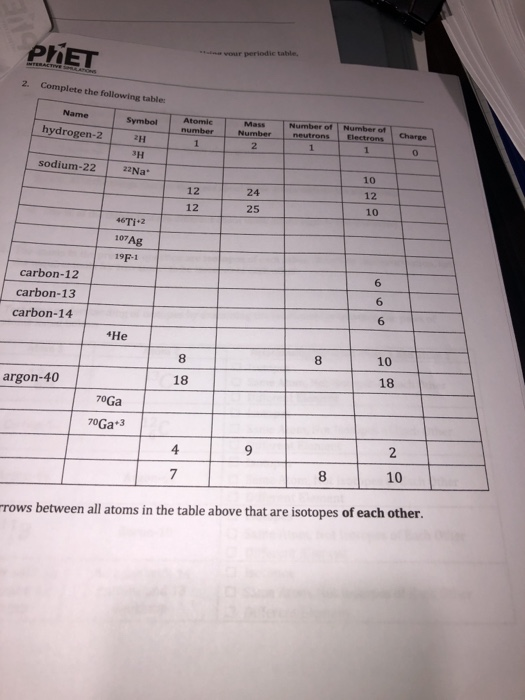
Which is the mass number of Sodium?
Sodium Neutron
22.98977 amu
Not too many people know the fact that the symbol for Sodium is Na. Needless to say, the atomic number is 11. Keep in mind that the atomic mass of Sodium is 22.98977 amu. Needless to say, the melting point of Sodium is 97.72 °C (370.87 K, 207.9 °F). On the contrary, the boiling point is 883 °C (1156 K, 1621 °F). There are 11 electrons in Sodium. Keep in mind that there are 12 neutrons in Sodium. Moreover, Sodium has a cubic crystal structure. The color of Sodium is silvery.
The mass number of an atom specifies the numbers of particles in the nucleus. It is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons. In scientific writing, the mass number is usually located to the upper left of an atom’s symbol. When given together with the atomic number, or the number of protons, the mass number tells an atom’s element and isotope.
An atom consists of protons, neutrons and electrons. Both protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom and have masses roughly 1,800 times larger than the more mobile electrons. Protons and electrons have opposite electrical charges; for an atom to be electrically neutral, the number of protons must equal the number of electrons. Neutrons have no electrical charge.
Now known as td bank na: bank of the west (california address only) see bk west c11006: bank of western mass. Now known as peoples united bank: bank one (all lienholder codes) now known as jp morgan chase bank na (c32643) bank ozk. Po box 242208 / little rock / ar 72223: bank ozk. 600 w commercial / ozark / ar 72949. The number of atoms or molecules (n) in a mass (m) of a pure material having atomic or molecular weight (M) is easily computed from the following equation using Avogadro's number (NA = 6.022×10 23 atoms or molecules per gram-mole): M mN n A (1) In some situations, the atomic number density (N), which is the concentration of atoms or molecules per.

The number of protons in an atomic nucleus determines which element the atom is. An atom with eight protons is an oxygen atom, for example. The number of neutrons in an atom, however, can vary somewhat and remain the same element; these varieties are called isotopes. An oxygen atom can contain eight, nine, or 10 neutrons and still be stable. Adding the number of protons and neutrons together gives the mass number.
Sodium Protons Neutrons Electrons
Atomic mass of Sodium is 22.9897 u. Atomic Data for Sodium (Na) Atomic Number = 11 Atomic Weight = 22.989768 Reference E95: Isotope: Mass: Abundance: Spin: Mag Moment: 23 Na: 22.989767: 100%: 3/2: 2.21752: Na I Ground State 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 S 1 / 2 Ionization energy 41449.451 cm-1 (5.139076 eV) Ref.
A convention is commonly used for representing information about atoms in writing. An atom’s symbol on the periodic table indicates the atomic number. The mass number is located in the superscript position to the left of the atom symbol. A net electrical charge, if present, is written in the superscript position to the right. These three pieces of information reveal the total number of protons, neutrons and electrons, respectively.
The existence of different isotopes is the result of radioactive decay. One of the four fundamental forces of nature, the weak nuclear force, causes atoms to release energy without any contact with other matter. In alpha decay, two protons and two neutrons escape an atom entirely. In beta decay, a neutron can change into a proton. In this case, the mass number will stay the same, but the atomic number will increase by one.
Sodium Atom
It is important to distinguish mass number from atomic mass. The mass number is always an integer with no associated units. The atomic mass is a measurement of an atom’s mass and must have units of mass. While any unit for mass is valid, the most common unit used for atomic mass is the atomic mass unit. One atomic mass unit is equal to 1.66 x 10-24 grams.
